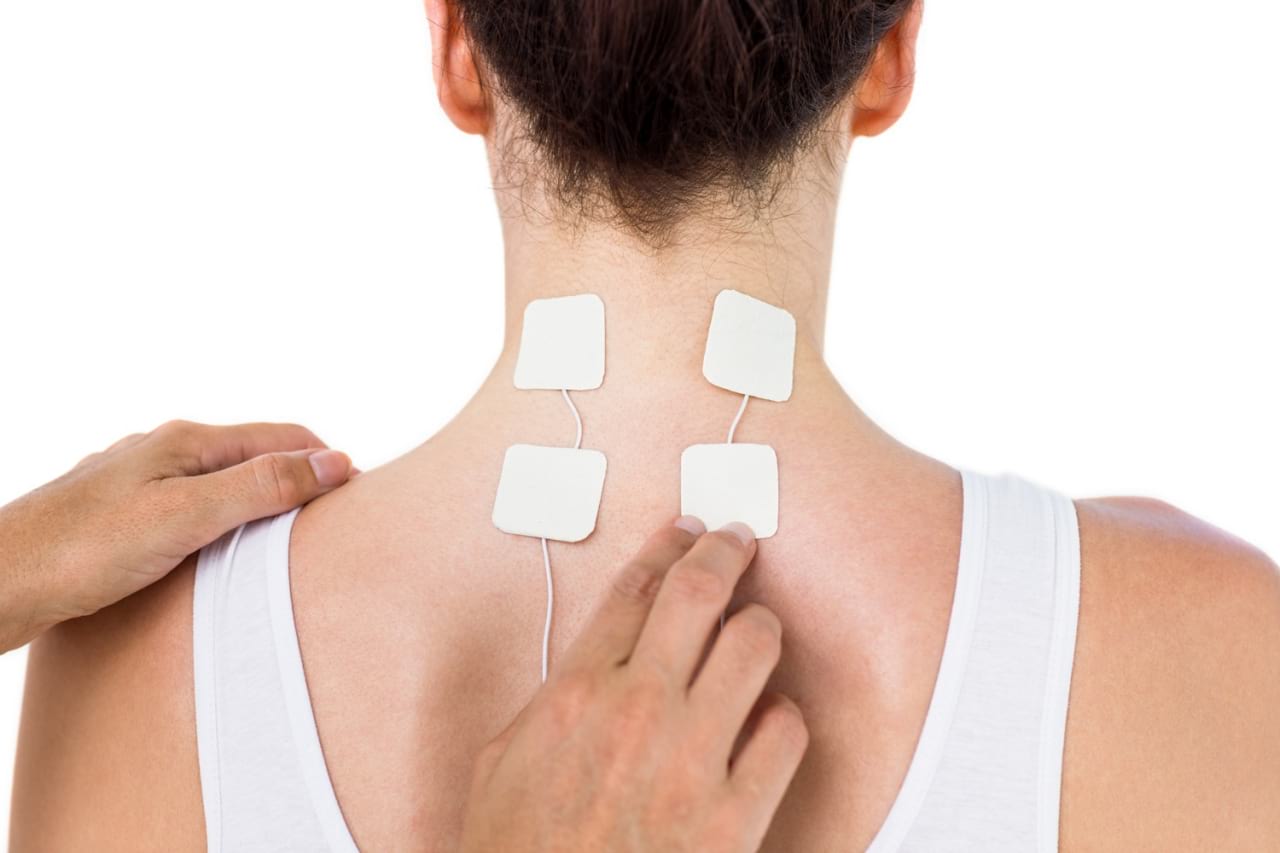
Only by conducting diagnostics can the cause of pain in the thoracic spine be clarified, since the symptoms of many pathologies are similar. Sometimes pain is caused by muscle stretching or spasms, but quite often it is caused by diseases of the spine, as well as the heart and lungs. For successful treatment, it is necessary to identify the disease as early as possible and begin appropriate therapy.
CAUSES OF PAIN IN THE THORACIC SPINE
In diseases of the spine, the pain can be either aching or sharp. It can be present constantly, weaken or intensify with certain movements. In addition to pain, other symptoms may also appear. For example, decreased mobility, crunching during movements, spread of pain to other parts of the body, and decreased sensitivity.
The causes of pain in the thoracic spine can be:
- spinal injuries;
- joint injuries;
- soft tissue damage;
- protrusions;
- herniated intervertebral discs;
- scoliosis and kyphosis;
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine;
- joint diseases;
- radiculitis and other diseases.
With such spinal diseases as protrusions and herniated intervertebral discs, the pain can be aching for a long time. However, it can intensify during movements and become acute with the development of complications, such as nerve entrapment.
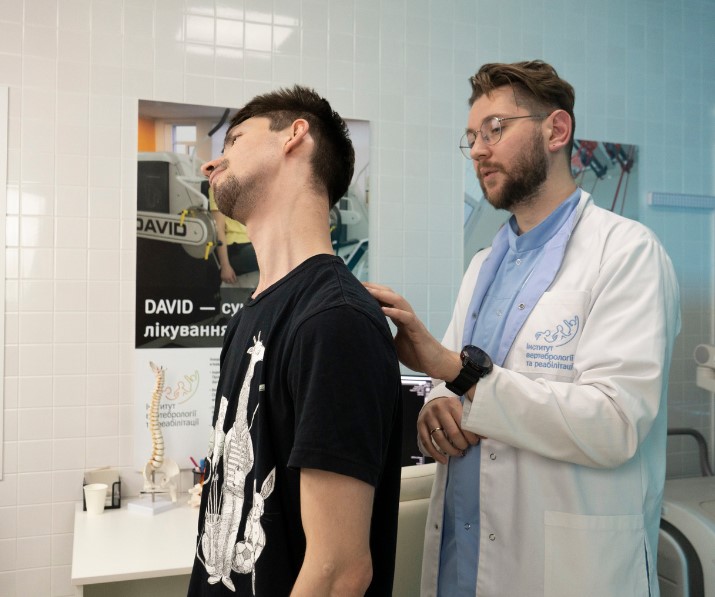
The symptoms of radiculitis are more specific. It is characterized by sharp and acute pain, as well as significant limitation of mobility. However, in the thoracic spine, it develops quite rarely.
In case of damage to soft tissues - muscles, ligaments and tendons, the pain is usually aching, not acute. It has a permanent character and can increase with their load.
Spinal injuries usually cause acute pain and require immediate medical attention to the patient. However, the cause of pain can also be old injuries that occurred many years ago. They can provoke the formation of muscle blocks and clamps, as a result of which other muscles, taking on a compensatory function, are in hypertonus. Over time, this becomes the cause of muscle pain, nerve entrapment and other complications.
The same applies to joint injuries. They can also eventually become the cause of severe pain. In this case, the injury itself can be minor and cause only a slight aching pain, however, without timely treatment and with further load, the condition can gradually worsen.

Pain in the chest can also be caused by other pathologies. For example:
- respiratory organs (bronchitis and pneumonia);
- heart and blood vessels;
- nervous system, in particular intercostal neuralgia, and other diseases.
TREATMENT FEATURES
Treatment of diseases of the spine and joints should be comprehensive. If you eliminate the symptoms, but do not carry out therapy for the underlying disease, it can worsen and soon lead to a new exacerbation.
First of all, if the back and chest are very painful, intensive therapy methods are used to quickly relieve acute symptoms. In this case, the patient can be given therapeutic blockades - injections of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs into the center of localization of the pathological process. They provide an almost instant pain relief.

During the initial examination, the doctor also learns about the patient's complaints and studies the medical history. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the data obtained in this way is sufficient to make a diagnosis.
There are clear signals and indications for the use of additional examination methods, which the doctor sees during the initial examination. Therefore, we do not recommend doing any examinations on your own before visiting a doctor.
The program of further treatment is developed by the doctor individually, taking into account the underlying disease, concomitant pathologies and other factors.
Treatment of protrusions, herniated intervertebral discs and scoliosis of 1-2 degrees is carried out in most cases by conservative methods and does not require surgery.
Treatment of radiculitis should include therapy not only of this syndrome, but also of the underlying disease. Radiculopathy does not develop on its own, but in the presence of another pathology of the spine.
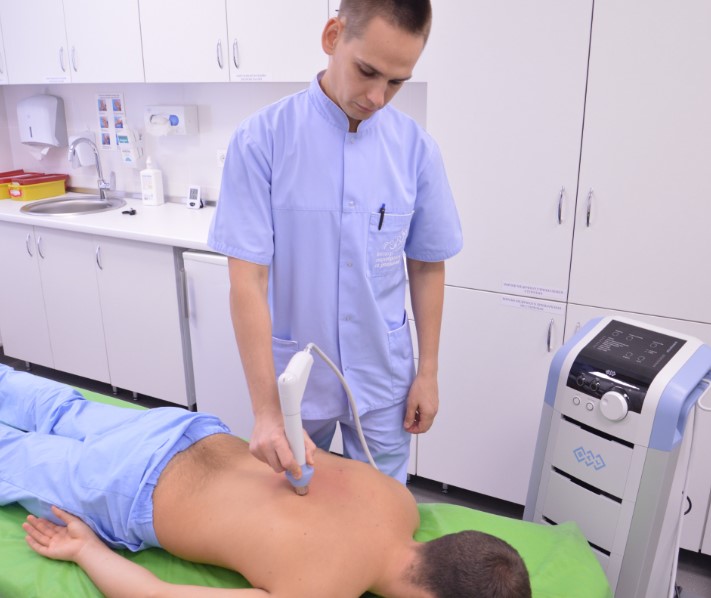
Thoracic osteochondrosis also needs to be treated not only symptomatically. With the right approach, it is possible to reduce the severity of pain and ensure the restoration of the structure and functionality of the spine.
The following are used to treat diseases of the spine and joints:
- gentle manual therapy techniques;
- therapeutic massage;
- hardware physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapy;
- kinesiotherapy;
- drug therapy (blockades, intramuscular injections, etc.)
Each technique has its own mechanism of action and ensures the achievement of a certain result. The best effect is achieved with complex treatment, when the influence on all links of the pathological